SpringMVC的执行流程源码分析
背景
一个常见的面试/笔试题: SpringMVC的执行流程
答:
1、前端请求到核心前端控制器DispatcherServlet
2、DispatcherServlet收到请求调用HandlerMapping处理器映射器。
3、处理器映射器找到具体的处理器,生成处理器对象及处理器拦截器(如果有则生成)一并返回给DispatcherServlet。
4、 DispatcherServlet调用HandlerAdapter处理器适配器。
5、HandlerAdapter经过适配调用具体的处理器(Controller,也叫后端控制器)。
6、Controller执行完成返回ModelAndView。
7、HandlerAdapter将controller执行结果ModelAndView返回给DispatcherServlet。
8、DispatcherServlet将ModelAndView传给ViewReslover视图解析器。
9、ViewReslover解析后返回具体View.
10、DispatcherServlet根据View进行渲染视图(即将模型数据填充至视图中)。
11、DispatcherServlet响应用户。
为了应付面试相信很多人和我一样死记硬背过,今天就来看下源码,看看这个流程的庐山真面目。
首先找到DispatcherServlet类,看看它的继承关系 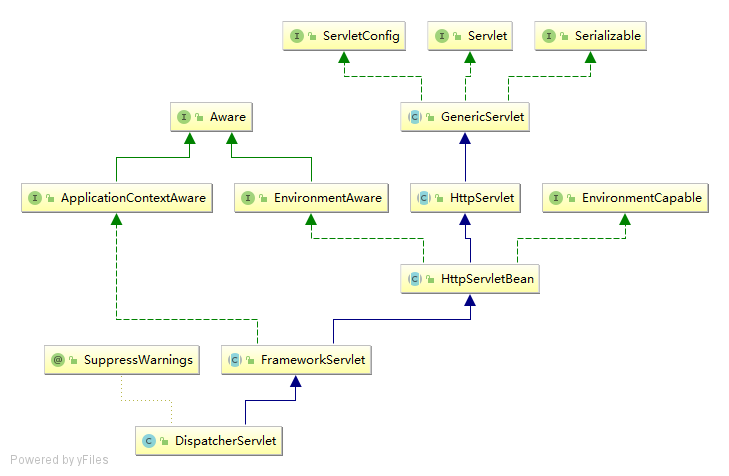
1.DispathcerServlet的初始化过程
过程图 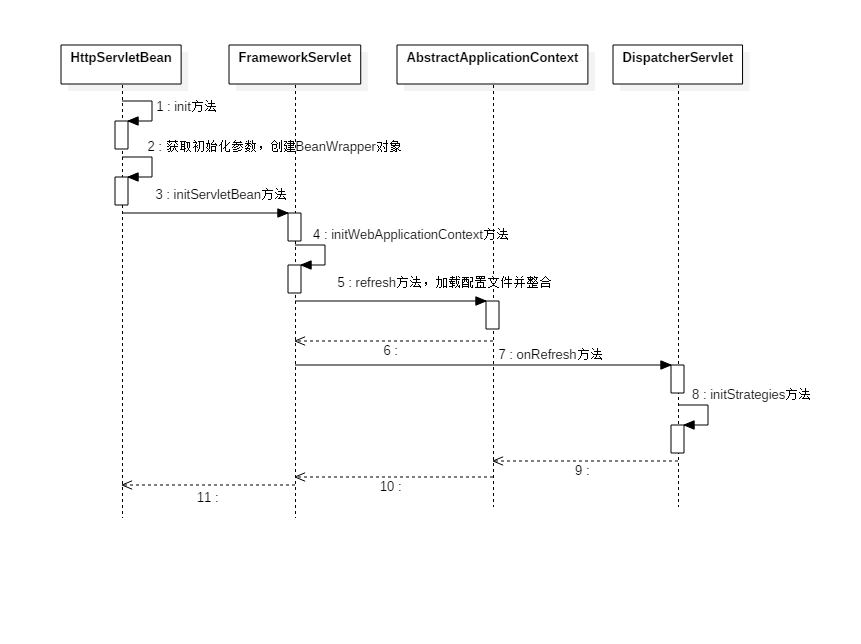
初始化方法
/**
* This implementation calls {@link #initStrategies}.
*/
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
/**
* Initialize the strategy objects that this servlet uses.
* <p>May be overridden in subclasses in order to initialize further strategy objects.
*/
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}可以看到initStrategies方法初始化了9个组件,其中不乏文章开头中问题涉及到的组件
这九个初始化方法做的事情如下:
- initMultipartResolver:初始化MultipartResolver,用于处理文件上传服务,如果有文件上传,那么就会将当前的HttpServletRequest包装成DefaultMultipartHttpServletRequest,并且将每个上传的内容封装成CommonsMultipartFile对象。需要在dispatcherServlet-servlet.xml中配置文件上传解
- initLocaleResolver:用于处理应用的国际化问题,本地化解析策略。
- initThemeResolver:用于定义一个主题。
- initHandlerMapping:用于定义请求映射关系。
- initHandlerAdapters:用于根据Handler的类型定义不同的处理规则。
- initHandlerExceptionResolvers:当Handler处理出错后,会通过此将错误日志记录在log文件中,默认实现类是SimpleMappingExceptionResolver
- initRequestToViewNameTranslators:将指定的ViewName按照定义的RequestToViewNameTranslators替换成想要的格式。
- initViewResolvers:用于将View解析成页面。
- initFlashMapManager:用于生成FlashMap管理器。
2.DispatcherServlet如何处理用户请求
首先要明确DispatcherServlet也是一个Servlet,也要遵守servlet接口的规范,servlet通过service方法来根据不同的请求方式来执行doGet,doPost等方法。而FrameworkServlet重写了service方法,并调用了processRequest方法,processRequest方法中又调用了抽象方法doService,DispatcherServlet实现了doService方法,并在该方法中调用了doDispatch方法,doDispatch方法就是具体的请求处理过程
过程图: 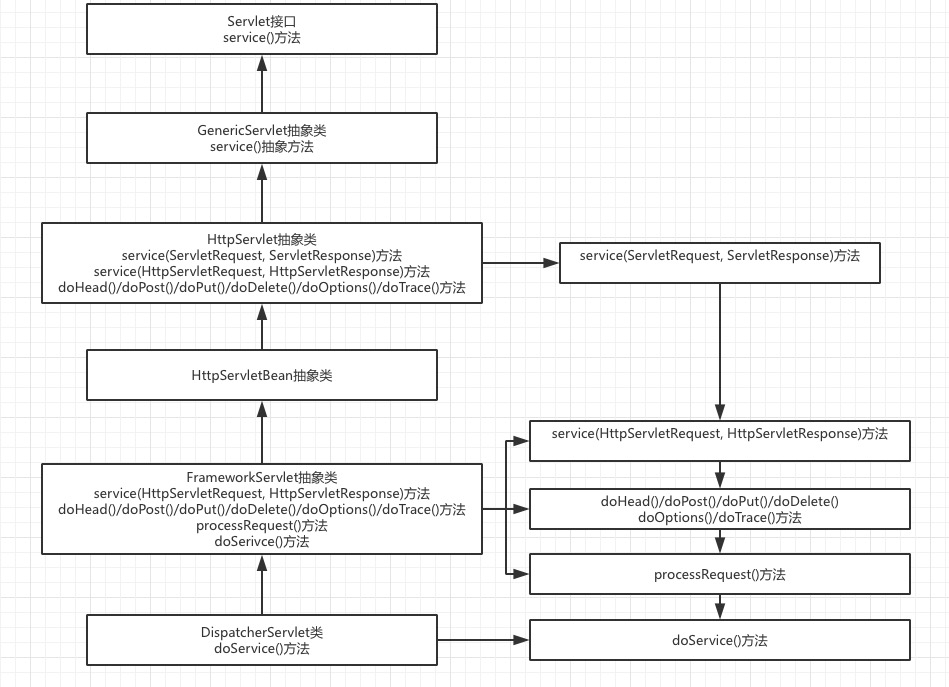
3.doDispatch方法
/**
* Process the actual dispatching to the handler.
* <p>The handler will be obtained by applying the servlet's HandlerMappings in order.
* The HandlerAdapter will be obtained by querying the servlet's installed HandlerAdapters
* to find the first that supports the handler class.
* <p>All HTTP methods are handled by this method. It's up to HandlerAdapters or handlers
* themselves to decide which methods are acceptable.
* @param request current HTTP request
* @param response current HTTP response
* @throws Exception in case of any kind of processing failure
*/
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
//判断是否为上传文件的请求,如果不是就返回原始的request,否则做相应的处理
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
//找到当前请求对应的处理器,返回的是对应的处理器及拦截器集合
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
//根据上一步找到的处理器,再找到对应的处理器适配器
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
//这里执行了所有的拦截器中的preHandle方法 也就是为什么拦截器总在controller前先执行
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
//调用处理器的处理方法
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
//设置modelAndView的默认名
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
//执行拦截器的postHanle方法
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
//处理modelAndView并渲染
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}1.getHandler方法
该方法返回的是HandlerExecutionChain对象,其中包含了处理器和过滤器的集合,这里调用了handlerMapping的getHandler方法,该方法主要调用了getHandlerExecutionChain方法,handlerMapping的集合是在初始化dispatchServlet的时候从beanFactory中查找并封装的,具体的handlerMappings初始化细节可以看initHandlerMappings方法,handlerMapping有多种类型,对应不同的请求,比如请求静态资源的和请求接口的等,此处我们以请求一个查询接口为例
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
//循环所有的handlerMapping,直到找到对应的handler
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}getHandlerExecutionChain方法
这里调用的是AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的getHandlerInternal方法,该方法又调用了同一个类中的lookupHandlerMethod方法
lookupHandlerMethod方法会根据请求的uri在mappingRegistry中查询已经注册了的请求路径(requestMapping注解中的路径),如果能直接从map中get到非空的list,就直接根据list匹配对应的HandleMethod对象,如果mappingRegistry中get不到,就尝试使用uri路径匹配,例如带有url参数的这种格式/test/{username}的格式,{username}会被替换为.*的正则表达式去进行匹配,匹配到后返回;
getHandlerExecutionChain方法则是根据请求的路径匹配拦截器的路径,如果有匹配到的,就添加到执行链当中
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//根据request找到对应的handler
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Mapped to " + handler);
}
else if (logger.isDebugEnabled() && !request.getDispatcherType().equals(DispatcherType.ASYNC)) {
logger.debug("Mapped to " + executionChain.getHandler());
}
if (CorsUtils.isCorsRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration globalConfig = this.corsConfigurationSource.getCorsConfiguration(request);
CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
CorsConfiguration config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig);
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ?
(HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler));
String lookupPath = this.urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request);
for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) {
if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) {
MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor;
if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, this.pathMatcher)) {
chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor());
}
}
else {
chain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
}
return chain;
}2.getHandlerAdapter方法
这个方法比较简单,就是从handlerAdapter集合中遍历找到支持当前请求的处理器适配器,用到了handlerAdapter的supports方法,测试的接口请求会调用AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter这个类的supports方法
/**
* This implementation expects the handler to be an {@link HandlerMethod}.
* @param handler the handler instance to check
* @return whether or not this adapter can adapt the given handler
*/
@Override
public final boolean supports(Object handler) {
return (handler instanceof HandlerMethod && supportsInternal((HandlerMethod) handler));
}3.handle方法
在找到对应的处理器适配器后,会执行拦截器的preHandle方法,然后执行处理器适配器的handle方法,这个就是实际上调用我们所写的controller了,该方法有几个实现  这里调用的是AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter的方法,该方法调用了抽象方法
这里调用的是AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter的方法,该方法调用了抽象方法handleInternal,它的实现在RequestMappingHandlerAdapter类中
protected ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
ModelAndView mav;
checkRequest(request);
// Execute invokeHandlerMethod in synchronized block if required.
if (this.synchronizeOnSession) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session);
synchronized (mutex) {
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
// No HttpSession available -> no mutex necessary
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
// No synchronization on session demanded at all...
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
if (!response.containsHeader(HEADER_CACHE_CONTROL)) {
if (getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod).hasSessionAttributes()) {
applyCacheSeconds(response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers);
}
else {
prepareResponse(response);
}
}
return mav;
}其中重点在invokeHandlerMethod方法,这个方法首先初始化了一个新的handlerMethod对象,添加了相关的解析组件,返回值处理器等等,然后执行了invokeAndHandle方法,然后最终调用了InvocableHandlerMethod类中的doInvoke方法
protected ModelAndView invokeHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response);
try {
WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod);
ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory);
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod invocableMethod = createInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod);
if (this.argumentResolvers != null) {
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers);
}
if (this.returnValueHandlers != null) {
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers);
}
invocableMethod.setDataBinderFactory(binderFactory);
invocableMethod.setParameterNameDiscoverer(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer();
mavContainer.addAllAttributes(RequestContextUtils.getInputFlashMap(request));
modelFactory.initModel(webRequest, mavContainer, invocableMethod);
mavContainer.setIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect(this.ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect);
AsyncWebRequest asyncWebRequest = WebAsyncUtils.createAsyncWebRequest(request, response);
asyncWebRequest.setTimeout(this.asyncRequestTimeout);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.setTaskExecutor(this.taskExecutor);
asyncManager.setAsyncWebRequest(asyncWebRequest);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptors(this.callableInterceptors);
asyncManager.registerDeferredResultInterceptors(this.deferredResultInterceptors);
if (asyncManager.hasConcurrentResult()) {
Object result = asyncManager.getConcurrentResult();
mavContainer = (ModelAndViewContainer) asyncManager.getConcurrentResultContext()[0];
asyncManager.clearConcurrentResult();
LogFormatUtils.traceDebug(logger, traceOn -> {
String formatted = LogFormatUtils.formatValue(result, !traceOn);
return "Resume with async result [" + formatted + "]";
});
invocableMethod = invocableMethod.wrapConcurrentResult(result);
}
invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer);
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return null;
}
return getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest);
}
finally {
webRequest.requestCompleted();
}
}- doInvoke方法
这里就比较明显了,首先利用暴力反射将方法设置为可访问的,然后直接反射调用并返回结果
/**
* Invoke the handler method with the given argument values.
*/
@Nullable
protected Object doInvoke(Object... args) throws Exception {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(getBridgedMethod());
try {
return getBridgedMethod().invoke(getBean(), args);
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
assertTargetBean(getBridgedMethod(), getBean(), args);
String text = (ex.getMessage() != null ? ex.getMessage() : "Illegal argument");
throw new IllegalStateException(formatInvokeError(text, args), ex);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
// Unwrap for HandlerExceptionResolvers ...
Throwable targetException = ex.getTargetException();
if (targetException instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) targetException;
}
else if (targetException instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) targetException;
}
else if (targetException instanceof Exception) {
throw (Exception) targetException;
}
else {
throw new IllegalStateException(formatInvokeError("Invocation failure", args), targetException);
}
}
}返回modelAndview对象后就是渲染的一些操作